이동통신 주요 시스템 개념
AuC (Authentication Center)
이동통신 망에서 가입자에 대한 인증 및 무선 통화 구간에 대한 암호화 기능을
지원(인증 키 관리)한다. 인증 및 암호화를 위하여, 자체 데이터베이스에서 가입자에 대한 전화번호, 단말기 일련번호, 인증 키
등을 관리하여, 정의된 인증 알고리즘을 수행한다.
BSC (Base Station Controller), 제어국
여러대의 기지국(BTS)들을 관리하면서 이동교환기(MSC)와 연동하며, 일부 제어국에서는 2.5 세대/3 세대 데이터서비스를 위하여 PDSN(라우터)과 연동 기능 제공
BTS (Base station Transceiver Subsystem), 기지국
이동전화와 무선 구간으로 연결되어 이동전화를 제어하고 통화 채널을 연결시켜주는 시스템
DSCP (Data SCP)
지능망 SCP와 연동하여, 선불형 지능망 가입자에 대한 세분화된 과금을 실시간 처리
EIR (Equipment Identification Register)
이동통신망에서 단말에 대한 IMEI
(International Mobile Station Equipment Identity)를 저장하고 관리한다. 부적절한 이동통신
단말기를 검출하고, 이들 단말에 대한 목록을 관리함으로써 부적절한 단말에 대한 사용을 제한하는 기능을 수행한다.
GMLC (General Mobile Location Center)
GMLC는 W-CDMA 망에서 SMLC(Serving Mobile
Location Center) 및 교환기, SGSN 등과의 연동을 통해서 가입자의 위치를 수집한다. 이는 이동 가입자(휴대폰)의
LBS 서비스 플랫폼의 가입자 위치정보 요청에 의하여 가입자의 위치 정보를 수집하여, LBS 서비스 플랫폼으로 전송 기능을
수행한다.
HLR (Home Location Register), 홈위치등록기
이
동전화가입자에 대한 정보 (이동성- 현재 위치- 정보, 인증 및 부가 서비스 정보 등)를 실시간으로 관리하는 시스템으로,
교환기는 HLR에게 가입자의 현재 위치 정보를 입수하여 이동통신 가입자에 대한 착신이 가능하게 된다. 내부 데이터베이스에는
가입자에 대한 전화번호, 단말기 일련번호, 호처리 루팅 정보, 권한 정보, 각종 부가서비스 정보 등을 관리한다.
INBH (Intelligent Billing Host)
선불형 지능망 가입자의 데이터 호(단문 메시지, 인터넷 컨텐츠,
장문 메시지 등)에 대한 실시간 과금을 수행한다. SMSC, VAS, LMSC 등 여러 종류의 Client와 연동하여 차감
금액을 실시간으로 계산하고, 이를 지능망 SCP에 전달한다.
IPAS (IP Accounting System)
다양한 특성을 가진 개별 서비스(IP address, 컨텐츠 내용, URL
등)에 대한 차등 과금을 수행한다. (컨텐츠 가치 중시) 데이터 망에서 전송되는 raw packet data를 실시간으로
캡쳐하고, 실시간으로 분석하여, 실시간으로 과금 처리하는 기능을 제공한다.
LMSC( Long Message Service Center), 장문메세지센터
장문 메시지 저장/전송 기능 제공한다. 단문메시지와 장문메시지의 구분 기분은 전송할 메시지가 80바이트를 넘는지의 여부이다.
MMS (Multimedia Message System), 멀티미디어메세지센터
멀티미디어 메시지 저장/전송 기능 제공
MPC (Mobile Positioning Center)
MPC
는 CDMA 망에서 측위 서버인 PDE(Positioning Determination Entity) 및 교환기와의 연동을 통해서
가입자의 위치를 수집한다. 이는 이동 가입자(휴대폰)의 LBS 서비스 플랫폼의 가입자 위치정보 요청에 의하여 가입자의 위치
정보를 수집하여, LBS 서비스 플랫폼으로 전송 기능을 수행한다.
MSC (Mobile Switching Center), 이동교환기
이동통신망의 핵심 망요소로서, 음성통화 및 각종 부가서비스를 제어하고,
통화로를 설정하며, 여러 다른 장비들 및 외부망과의 연결기능을 제공한다. 즉, MSC는 이동통신 가입자에게 회선교환 서비스 및
통화채널 전환 기능을 제공하는 교환기이다.
SMSC (Short Message Service Center), 단문메세지센터
단문 메시지 저장/전송 기능 제공한다. 단문메시지와 장문메시지의 구분 기분은 전송할 메시지가 80바이트를 넘는지의 여부이다.
VLR (Visitor Location Register)
방문 가입자에 대한 호처리를 위한 위치레지스터 시스템
□ 지능망
지능망(Intelligent Network)이란 이동통신교환기(MSC)의
소프트웨어 변경 없이 새로운 서비스를 이동통신망에 적용할 수 있는 망 환경을 의미한다. 지능망이란 용어는 CDMA의 경우
WIN이란 규격, GSM의 경우 CAMEL이란 규격으로 발전되었다.

Dual Stack SCP (CDMA WIN & W-CDMA CAP)
CDMA 지능망 서비스(WIN)와 W-CDMA
지능망 서비스(CAMEL)를 하나의 플랫폼에서 동시에 제공하는 SCP 시스템이다. 이 시스템은 CDMA 서비스와 W-CDMA
서비스를 동시에 제공하는 사업자가 망 투자비를 절약할 수 있는 솔루션이다.
IP (Intelligent Peripheral)
지능망 서비스에 필요한 각종 안내 멘트를 제공한다. 지능망 서비스 진행을 위한 비밀번호, 서비스 선택 등의 각종 정보를 가입자로부터 수집한다.
Parlay GW & AS / Parlay X GW & AS
외부 서비스개발업체(3rd Party CP)들에게 표준화된 연동 규격(Open API)을 제공하여 망 플랫폼과 서비스 플랫폼의 종류에 상관없이 다양한 신규 부가 서비스들을 제공할 수 있게 해주는 차세대 지능망 솔루션이다.
SCP (Service Control Point)
지능망의 핵심 장비로써, 각종 서비스에 대한 서비스
로직을 제공한다. 즉, 이동통신 사업자의 지능망 서비스 시나리오를 실제로 수행한다. 교환기(SSP)와의 연동을 통하여 서비스
수행에 필요한 호처리를 수행하며, IP를 제어하여 가입자에게 안내방송을 제공한다.
Service Node
한 두 개의 특정 지능망 서비스를 도맡아 수행하는 시스템으로써, 해당 서비스에 대해서는 지능망의 SCP/IP/SMP의 기능을 모두 수행한다.
SMP (Service Management Point)
고객센터와의 연동을 통하여 가입자 정보를 저장 및 관리하고, 이를 다수의 SCP에 분배한다. 통합된 운영 및 유지보수 기능을 사용하여, 다수의 SCP 및 IP에 대한 관리가 가능하도록 한다.
□ IMS망
IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS)는 IP를 기반으로 다양한
멀티미디어 서비스를 제공할 수 있도록 하는 core network infra이다. 사용자는 저렴한 비용으로 다양하면서 풍부한
서비스를 사용할 수 있는 사업자를 선호하게 될 것이며, 이러한 변화에 대한 정확한 해답이 바로 IMS이다.
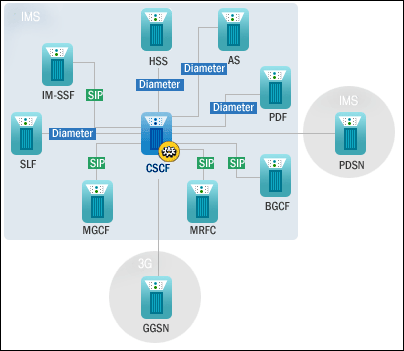
<3GPP의 IMS 망 구조>
BGCF (Breakout Gateway Control Function)
PSTN 착신호에 대한 라우팅 최적화를 고려하여 적당한 MGCF를 선택
IBCF
IMS 망간 연동을 위한 보안 및 NAT traversal 기능
CSCF (Call Session Control Function)
3G 네트워크 상에서 SIP 기반의 Call Control 및 Session Handling기능을 수행하는 시스템으로 다양한 멀티미디어 서비스를 제공 가능하게 한다.
IP-CAN(IP-Connectivity Access Network)
이동 단말이 IMS 망에 접속하기 위해서는 IP-CAN을 거쳐야 한다. IP-CAN은 단말에게 패킷데이터전송을 위한 엑세스망을 말한다. 예를 들어 GPRS나 WCDMA가 될 수 있다.
IMS-MGW / MGW (Media Gateway)
MGW는 PSTN이나 2G/2.5G 망과 연동하기 위해서 IMS 내의 IP 패킷 형태의 미디어 데이터(RTP)를 회선 교환망의 베어러 상에 전송될 수 있는 형태로 변환하는 기능을 한다. 이 과정에서 코덱의 변환이 필요하다.
I-CSCF (Interrogating-CSCF)
I-CSCF는 망 내의 가입자에게 연결하기
위해서 들어오는 모든 호에 대해서 접점 역할 및 망 내에 로밍한 타망 가입자와의 접점 역할을 수행한다. 이러한 역할로 인해서
일반적으로 I-CSCF는 방화벽(firewall) 역할을 수행하며 사업자 망의 구성, 토폴로지 및 용량 등을 외부에 노출되지
않게 하는 은닉기능을 가질 수 있다. I-CSCF는 HSS를 조회하여서 S-CSCF를 결정하고 등록과정에서 UE에게
S-CSCF를 할당하게 된다. 또한 SIP Request를 S-CSCF로 포워딩하는 역할 및 과금 정보의 생성을 수행한다.
그리고 여러 개의 HSS가 운용되는 망에서 SLF를 조회함으로써 HSS를 결정하는 역할을 한다.
MGCF (Media Gateway Control Function)
MGCF는 프로토콜 변환(SIP↔ISUP 시그널링
변환)을 처리하므로 PSTN과 PLMN 또는 SS7과 IP의 종단점으로 정의할 수 있다. 이는 PSTN에서 IMS으로 들어오는
호에 대한 시그널링의 변환 및 변환된 Request 메시지를 S-CSCF로 포워딩하는 기능을 수행하고, IMS와 PSTN 간의
호 제어 시그널링에 의해서 생성되는 호의 실질적인 베어러의 연결을 위해서 MGW를 제어한다.
MRF (Multimedia Resource Function)
MRF는 IM Subsystem 상에서
다자간 멀티미디어 회의를 제어하고 미디어 데이터를 처리하는 기능을 담당한다. 주요한 기능으로는 멀티미디어 메시지 재생, 음성메일
서비스, 미디어 변환/믹싱 서비스, Transcoding 서비스를 한다. 또한 기존의 MSC가 가지고 있던 Tone 생성 및
안내방송 기능도 담당한다.
P-CSCF (Proxy-CSCF)
P-
CSCF는 단말이 GPRS 액세스를 통해서 IMS에 접속할 때 처음 만나는 지점이다. 3GPP에서는 단말이 P-CSCF를 찾는데
DHCP를 이용하거나 PDP Context를 통해서 주소를 얻는 방법을 제시하고 있다. 단말로부터의 SIP Register
Request를 단말의 홈 도메인의 I-CSCF로 전달하고 이 등록절차에서 S-CSCF의 주소를 저장했다가 UE로부터
S-CSCF로 향하는 SIP 메시지가 있을때 이를 S-CSCF로 포워딩한다.
S-CSCF (Serving-CSCF)
S-
CSCF는 호 처리를 위한 주요기능을 수행하고, 서비스를 제공하기 위해서 관련되는 모든 기능에 대한 책임을 갖고 있다. 실제
등록된 사용자의 세션 상태관리를 하면서 제어 서비스를 수행하며, 사용자에게 서비스 자원과 관련된 정보를 제공한다. 사용자의
다이얼된 번호나 SIP URL을 통하여 착신 사용자의 홈 도메인의 I-CSCF의 주소를 얻는다.
SGW (Signaling Gateway)
SGW는 시그널링 프로토콜의 전송계층을 변환하는 기능을 수행한다. 즉, ISUP나 MAP과 같은 프로토콜 자체는 변환하지 않고 IP 망과 PSTN, IP 망과 기존망(2G 및 2.5G)의 전송계층을 변환하는 기능을 한다.
SLF (Subscription Locator Function)
망내에 HSS가 두 개 이상 운영되고 각각 별도의 주소로 인식될 때 CSCF에게 적절한 HSS의 주소를 제공
□ 데이터망
이동통신 망에서 데이터 서비스를 제공하기 위한 이동통신 인프라를 의미한
다. 음성통화를 주된 목적으로 했던 초기 휴대폰은 진화에 진화를 거듭하여 현재는 데이터 서비스 분야에서 더욱 많은 활용가치를
창출해가고 있다. 인터넷 가입자의 폭발적인 성장에 힘입어 무선 인터넷이 차세대 산업 분야로서 예견되고 있으며, 이러한 무선
인터넷 서비스를 제공하기 위한 기반 인프라를 통틀어 데이터 망이라 한다.
 <데이터망 구조>
<데이터망 구조>
AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting)
2G 및 1x 패킷 데이터 망에서 가입자 인증, 가입자 권한 확인, 과금 부여의 기능을 수행하는 무선 인터넷의 필수 망 요소의 하나이다. 즉, 가입자가 핸드폰을 사용하여 무선 인터넷에 접속할 경우, 1) 해당 가입자가 적법한지, 2) 해당 가입자에게 어떤 종류의 서비스가 제공 가능한지, 3) 얼마 만큼의 데이터 서비스를 받았는지를 결정하는 시스템이다.
DRN (Data Roaming Node)
W-CDMA망에서 해외로 로밍한 경우에도 데이터
서비스를 받을 수 있도록 해주는 시스템으로서, IM-GSN (Intermediate GRPS Serving Node)의 기능을
수행한다. 다른 PLMN 가입자의 Roaming 시 패킷 착신이 가능하도록 visited SGSN 과 home SGSN 간에
GTP 메시지를 중계하는 기능을 제공하며, 방문한 PLMN에서 동작한다.
GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node)
SGSN과 PDN 사이의 무선 게이트웨이 역할을 하는 GPRS 망 실체. 이
GGSN을 이용하여 이동 가입자가 PDN을 접속할 수 있다. GPRS 망에서는 외부망과 게이트웨이 역할을 담당하는 GGSN을
통하여 인터넷과 접속한다. 다시말해 GGSN은 패킷 데이터를 인터넷망으로 보내기 위한 게이트웨이 장치이다.
HSS (Home Subscriber Server)
HSS는 사용자에 대한 마스터 데이터베이스 역할을 수행하는 시스템으로, 2G
망의 HLR과 AuC 기능이 통합된 형태의 시스템이다. HSS는 이동성 관리, 사용자 인증 정보 생성, 서비스
Provisioning, 서비스 인증, 접속 권한부여 및 Call/Session 설정 지원 기능 등을 수행한다.
HSS는 3G HLR 기능을 모두 포함함과 동시에 IMS 가입자에 대한 정보를 관리하는 HLR의 super set이라고 볼 수 있다.
IWF (InterWorking Function system)
2 세대 데이터 서비스를 제공을 위한 모뎀 및 라우팅 기능 제공한다. 구형 모델의 휴대폰(예 : 흑백폰) 상에서의 데이터 서비스는 IWF를 통해서 IP 망과 연동하여 제공
PDSN (Packet Data Serving Node)
동기식 (CDMA) 1x 망에서 데이터 서비스를 제공하기 위해 네트워크 자원의
할당과 단말의 이동성을 관리하고 과금 정보를 수집해서 AAA로 전달한다. H/W 측면에서 보면 PDSN은 2.5 세대 및 3
세대 데이터 서비스를 제공하기 위한 라우터이다. 현재 대다수 컬러폰들이 PDSN과 연동한다.
SGSN (Support GPRS Serving Node)
SGSN은 비동기망(W-CDMA, UMTS,
GPRS등)에서 패킷 데이터 처리를 수행하는 시스템으로, 음성 서비스 분야의 교환기에 해당하는 역할을 수행한다. 이는 GGSN과
함께 GPRS 네트워크에서 초고속 인터넷 서비스를 가능케 하는 시스템 요소이다.